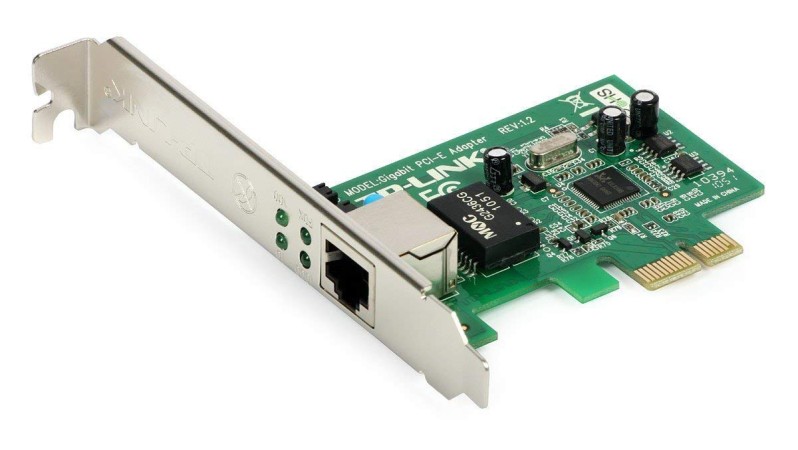
Alright, let’s talk about NICs—the unsung heroes of networking. NIC stands for Network Interface Card, but don’t let the boring name fool you. Without NICs, your devices wouldn’t have a clue how to connect to a network. They’re like the translators of the digital world, turning device signals into something the network understands.
Let’s break it down step-by-step and nerd out about how these tiny components make all the magic happen.
What Is a NIC?
At its core, a NIC (Network Interface Card) is the hardware that lets your computer or device connect to a network. It’s like the middleman between your device and the internet (or any network). Every device with network capabilities—your laptop, gaming console, even your smart fridge—has a NIC built in.
Why Do We Need NICs?
Imagine trying to shout into a walkie-talkie in a language it doesn’t understand. That’s your device without a NIC. The NIC’s job is to format and transmit data in a way that networks understand.
There are two main types:
- Wired NICs: These use Ethernet cables for fast and reliable connections.
- Wireless NICs: These connect via Wi-Fi for more flexibility.
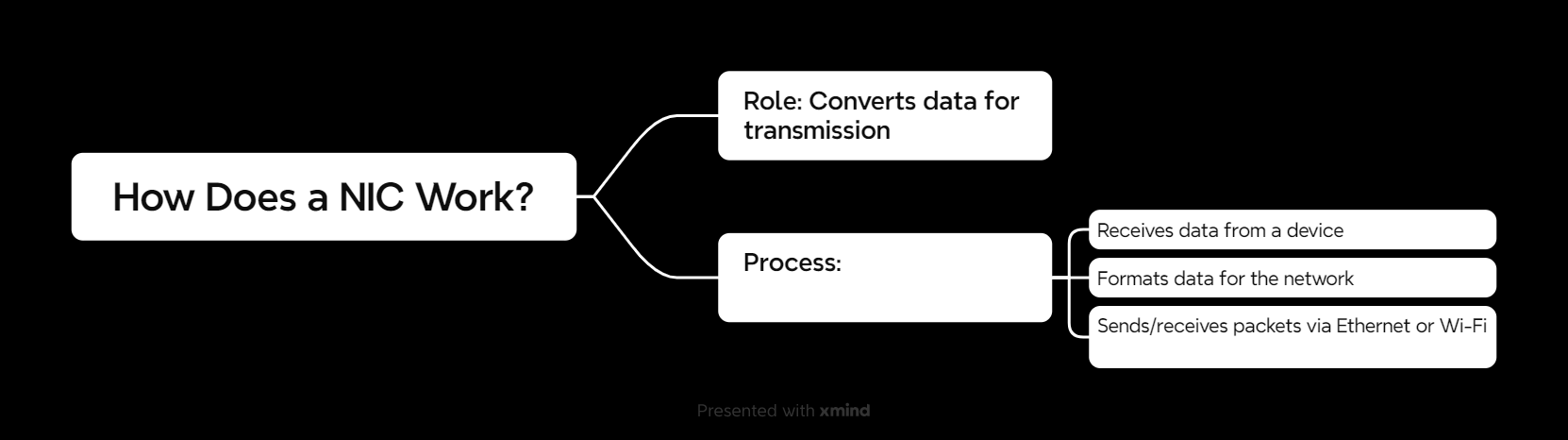
How Does a NIC Work?
Here’s the process in simple terms:
- Receiving Data: The NIC takes data from your device, like a file you want to upload or a webpage request.
- Formatting Data: It converts this data into packets that can travel across the network.
- Sending Data: The NIC sends these packets to the router or switch via Ethernet (wired) or Wi-Fi (wireless).
- Receiving Packets: When data comes back (e.g., a website loads), the NIC decodes it and sends it back to your device.
It’s like your NIC is having a constant conversation with the network—sending and receiving packets 24/7.
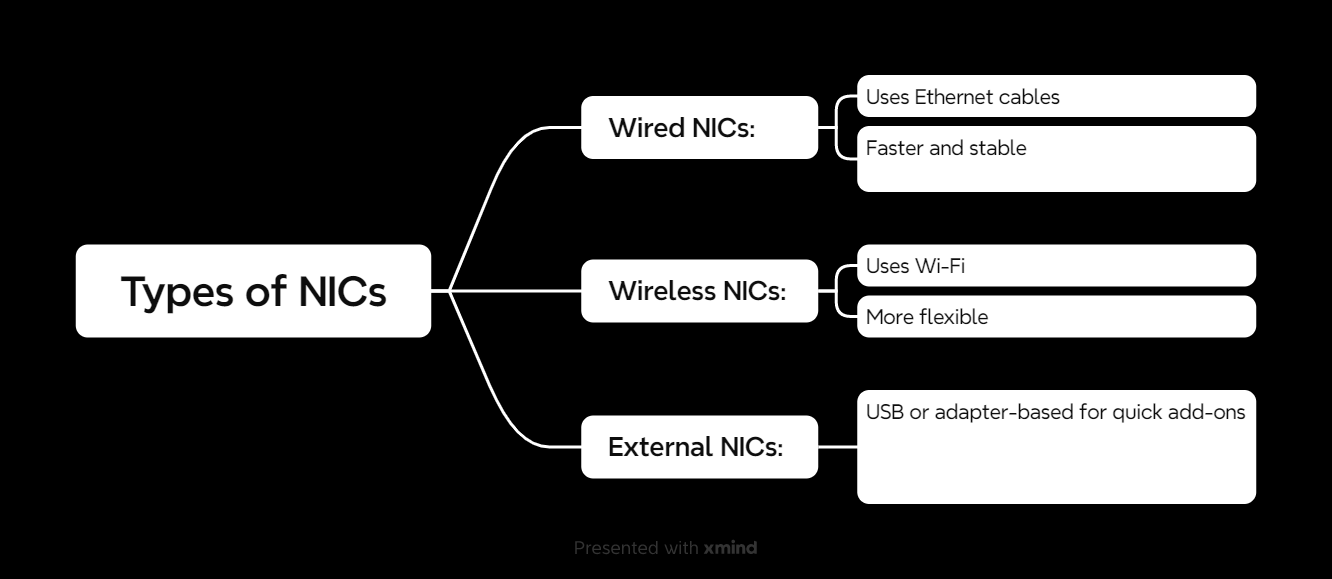
Types of NICs
NICs come in all shapes and sizes depending on the device and its purpose. Here are the main types:
1. Wired NICs
- What They Are: These use Ethernet cables for a direct connection.
- Benefits: Super fast and reliable, great for gaming or streaming.
- Downsides: You’re tied to a cable.
2. Wireless NICs
- What They Are: These connect via Wi-Fi, ditching the cables.
- Benefits: Freedom to move around, perfect for laptops and phones.
- Downsides: Slower than wired connections and can be affected by interference.
3. External NICs
- What They Are: Plug-and-play NICs that connect via USB or other ports.
- Benefits: Quick to add to a device without built-in networking.
- Downsides: Can be bulky or slower than internal NICs.
NICs in Action
NICs aren’t just sitting around—they’re doing work everywhere! Here’s where they shine:
- In PCs/Laptops: Connecting to the internet, downloading files, streaming videos.
- In Servers: Handling massive amounts of data and supporting enterprise networks.
- In IoT Devices: Helping smart devices talk to each other and the internet.