Let’s talk about the underrated superheroes of networking: cables. Whether you’re gaming, streaming, or running a massive server room, the right network cable can make or break your connection. So, let’s dive into the different types, how they work, and why you’d pick one over the other.
Why Do Network Cables Matter?
Network cables are like the highways for your data. They physically connect your devices, transferring information between them and the broader internet. While Wi-Fi is great for convenience, cables are still king when it comes to speed, reliability, and security.
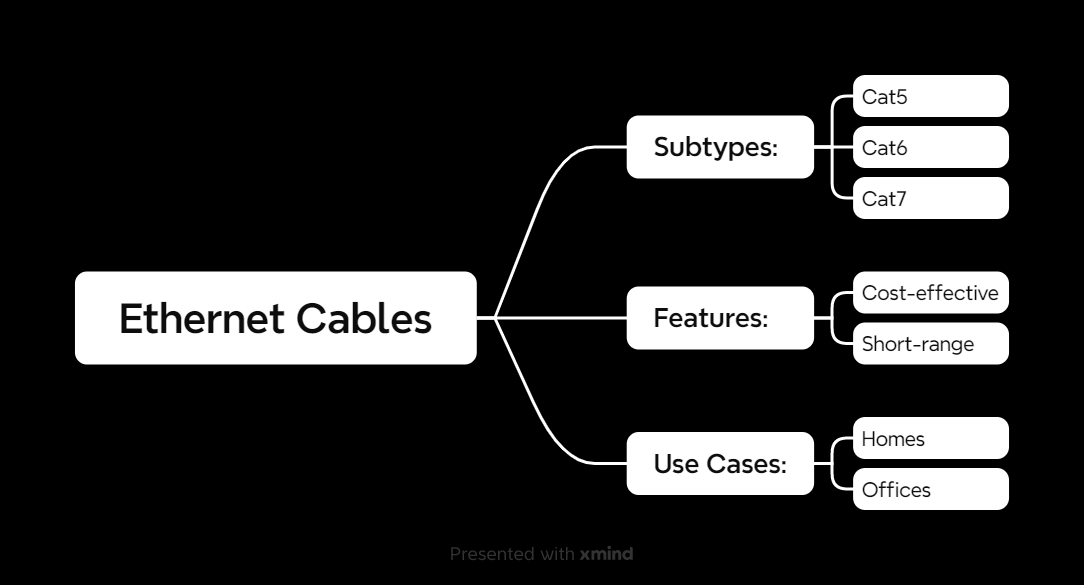
Ethernet Cables
Ethernet cables are the most common type you’ll see. They’re affordable, easy to use, and perfect for homes, offices, and even some data centers.
Types of Ethernet Cables
- Cat5: Old-school, supports speeds up to 100 Mbps.
- Cat5e: Enhanced version with speeds up to 1 Gbps.
- Cat6: Handles up to 10 Gbps, great for modern setups.
- Cat7: Future-proof, supports speeds beyond 10 Gbps.
Use Cases
- Home Networks: Connecting routers to PCs, gaming consoles, and smart TVs.
- Office Networks: Linking workstations for fast file sharing and printing.
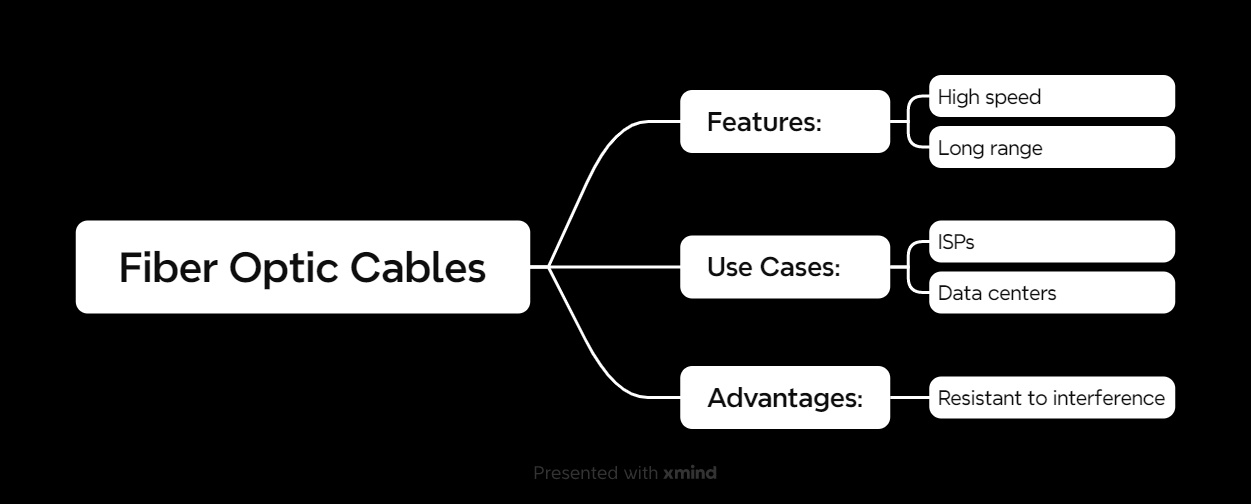
Fiber Optic Cables
Fiber optic cables are like the Ferraris of the networking world—fast, sleek, and built for performance. They use light to transmit data, which means blazing speeds and long ranges.
Features of Fiber Optic Cables
- Speed: Handles up to 1 Tbps.
- Range: Can transmit data over kilometers without losing quality.
- Interference Resistance: Immune to electromagnetic interference.
Use Cases
- ISPs: Delivering high-speed internet to homes and businesses.
- Data Centers: Managing huge amounts of data efficiently.
- Long-Distance Communication: Undersea cables connecting continents.
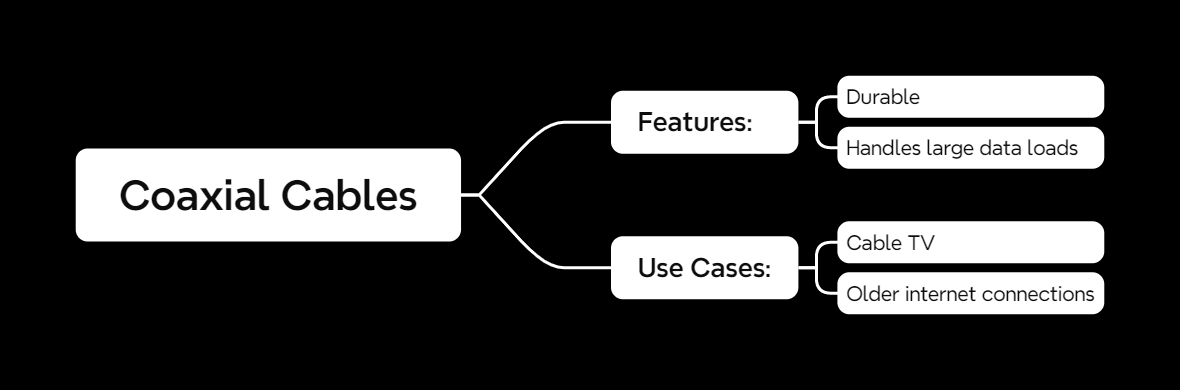
Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables might sound old-school, but they’re still super relevant for certain applications. They’re durable, reliable, and can handle large data loads.
Features of Coaxial Cables
- Construction: A core wire surrounded by insulation, shielding, and an outer layer.
- Durability: Built to last, even in tough environments.
Use Cases
- Cable TV: Used by providers to deliver TV signals.
- Older Internet Connections: Some ISPs still use them for broadband.
Choosing the Right Cable
So, which cable should you use? It depends on your needs:
- For Home Networks: Ethernet cables (Cat5e or Cat6) are your best bet.
- For High Performance: Fiber optics, especially for businesses or gaming.
- For Legacy Systems: Coaxial cables if you’re dealing with older tech.