Let’s dive into one of the most foundational concepts in networking: the OSI Model. Whether you’re a networking newbie or a seasoned geek, understanding the OSI model will level up your knowledge.
What Is the OSI Model?
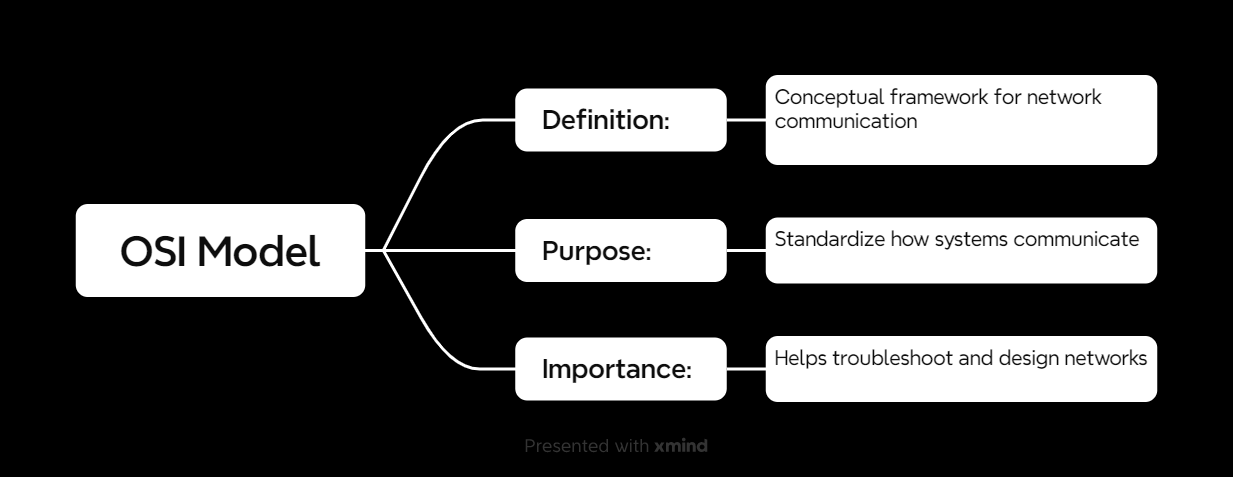
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is like the Rosetta Stone of networking. It’s a conceptual framework that breaks down communication into seven distinct layers, each with its specific role.
Why do we need it? Because without it, network communication would be a chaotic free-for-all. The OSI model ensures everyone’s speaking the same “language.”
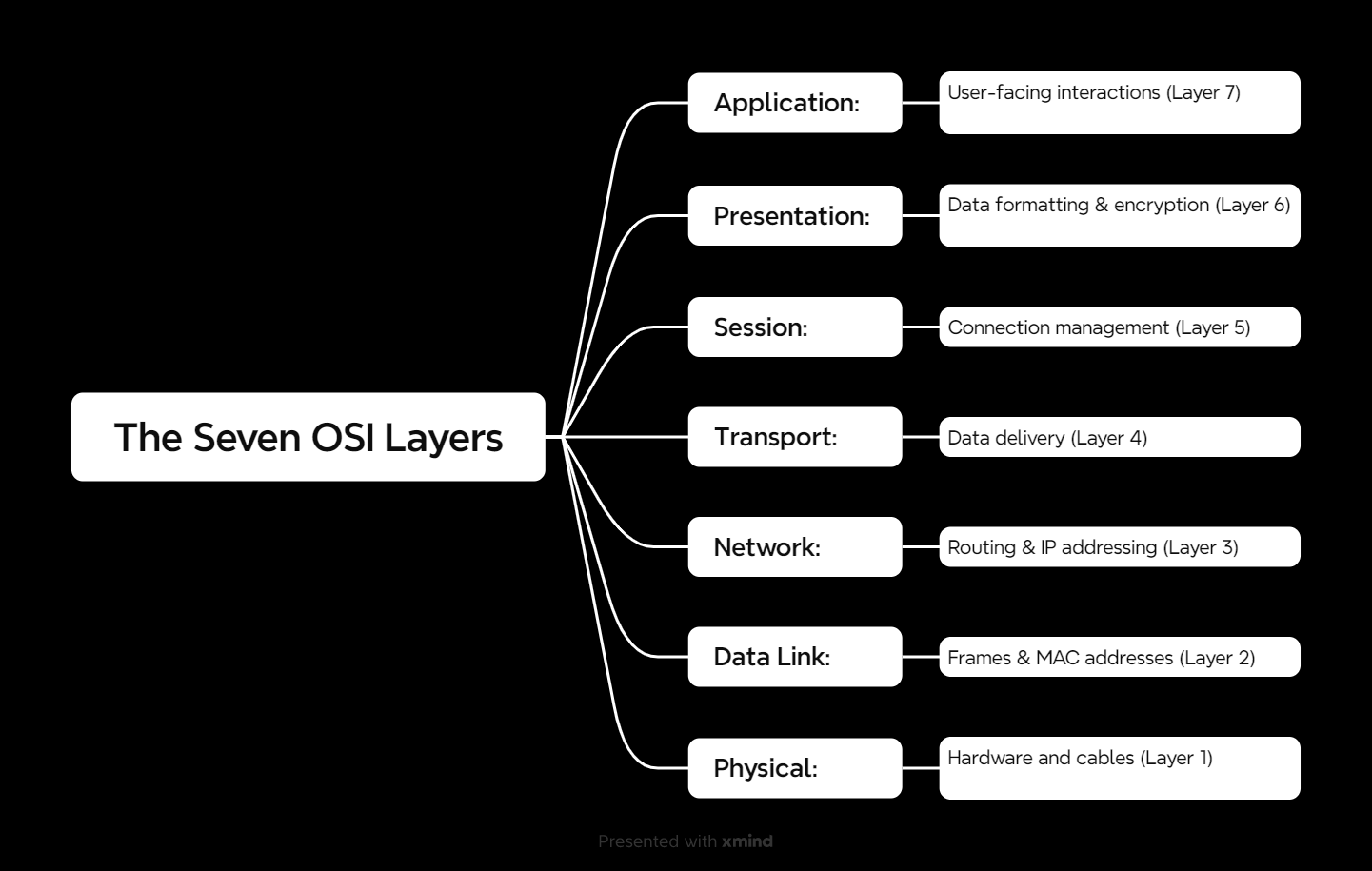
The Seven Layers of the OSI Model
Here’s a breakdown of the layers, from top (user-facing) to bottom (hardware-level):
1. Application (Layer 7)
- What It Does: Handles user-facing interactions like web browsers and email clients.
- Examples: HTTP, FTP, SMTP.
2. Presentation (Layer 6)
- What It Does: Translates data formats (e.g., encryption, compression). Think of it as the translator between apps.
- Examples: SSL/TLS, JPEG, MP3.
3. Session (Layer 5)
- What It Does: Manages sessions or connections between devices.
- Examples: NetBIOS, RPC.
4. Transport (Layer 4)
- What It Does: Ensures data delivery—either reliable (TCP) or fast (UDP).
- Examples: TCP, UDP.
5. Network (Layer 3)
- What It Does: Handles routing, IP addressing, and determining paths.
- Examples: IP, ICMP, RIP.
6. Data Link (Layer 2)
- What It Does: Organizes data into frames and manages MAC addresses.
- Examples: Ethernet, PPP, VLAN.
7. Physical (Layer 1)
- What It Does: Focuses on the actual hardware—cables, switches, and voltage.
- Examples: Ethernet cables, Wi-Fi frequencies.
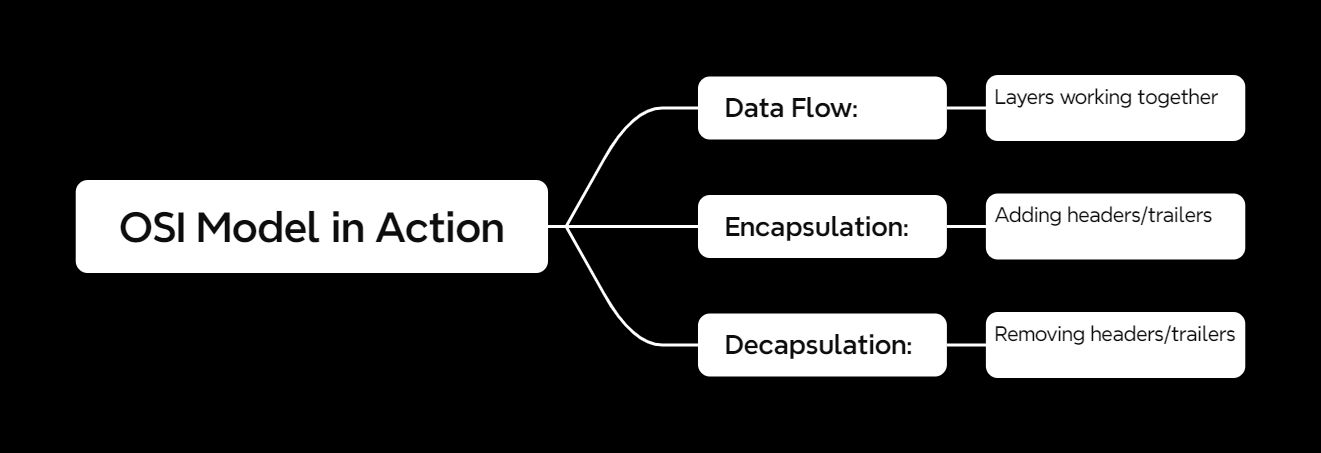
How the OSI Model Works
The OSI model is all about layers working together. Here’s how it flows:
1. Encapsulation
When data is sent, it travels down the layers, and each layer adds its own header or trailer.
2. Decapsulation
When data is received, it moves up the layers, and each layer strips off its own header or trailer.
3. Teamwork
Each layer only talks to the layer directly above or below it. This modular design makes troubleshooting and upgrades easier.
Why Is the OSI Model Important?
The OSI model isn’t just theoretical—it’s a practical tool for understanding networks.
1. Troubleshooting
The OSI model helps pinpoint where problems are occurring. Is it a physical issue (Layer 1)? Or maybe a routing issue (Layer 3)?
2. Network Design
When building networks, the OSI model ensures every aspect is accounted for—from hardware (Layer 1) to applications (Layer 7).
3. Protocol Mapping
Different protocols operate at different layers, and the OSI model helps categorize them.