Alright, let’s talk about the TCP/IP model, the rockstar of networking frameworks. If the OSI model is the nerdy academic, TCP/IP is the chill, street-smart sibling that everyone actually uses. Here’s how it stacks up against the OSI model and why it’s so important.
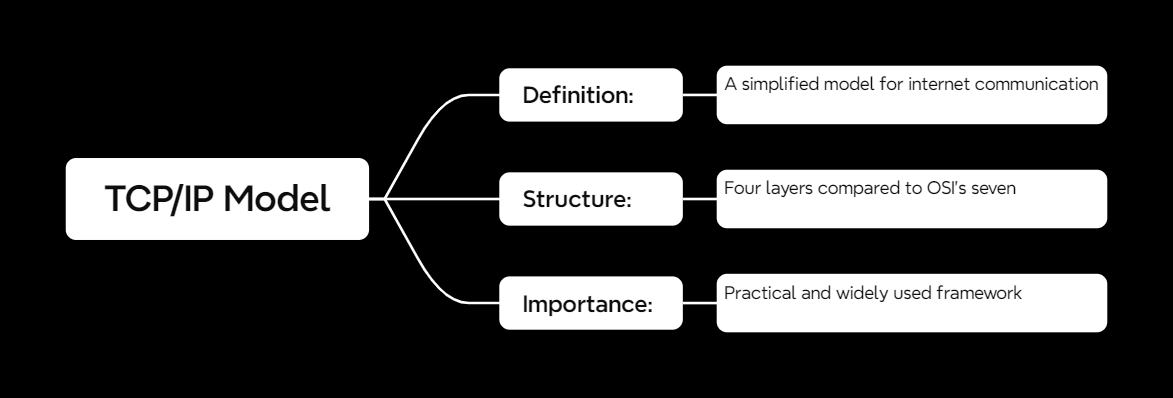
What Is the TCP/IP Model?
The TCP/IP model (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) is a simplified framework for network communication. It’s built to be practical and focuses on how the internet actually works.
Unlike the OSI model, which is more about understanding concepts, TCP/IP is the framework in action. It’s what keeps the internet running smoothly.
The Layers of the TCP/IP Model
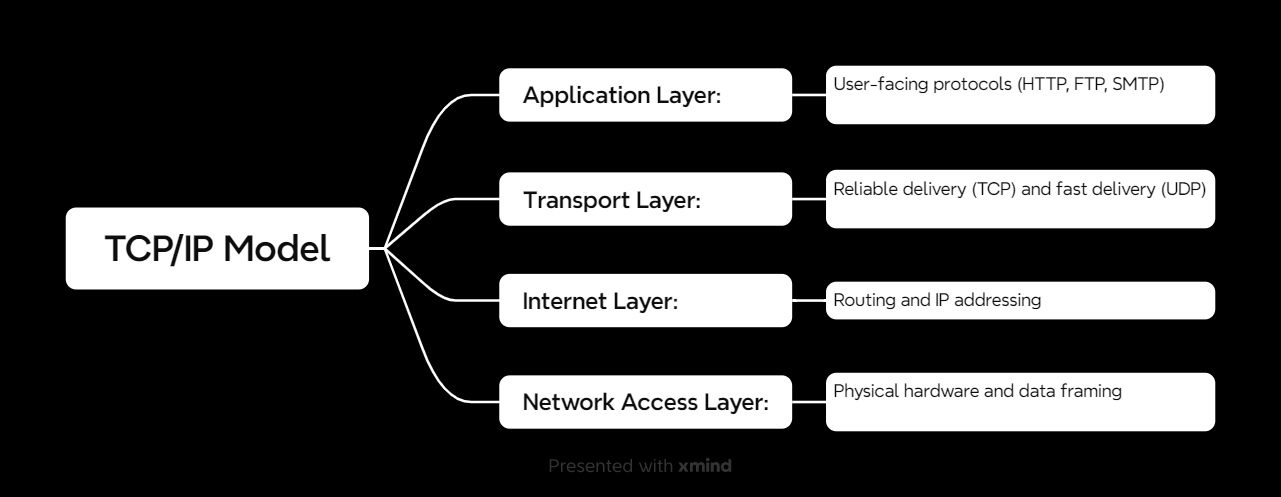
The TCP/IP model has four layers, compared to the OSI model’s seven. Here’s the breakdown:
1. Application Layer
- What It Does: Handles user-facing protocols like web browsing, email, and file transfers.
- Examples: HTTP, FTP, SMTP, DNS.
2. Transport Layer
- What It Does: Ensures data delivery is reliable (via TCP) or fast (via UDP).
- Examples: TCP, UDP.
3. Internet Layer
- What It Does: Handles IP addressing and routing to ensure data reaches the right destination.
- Examples: IP, ICMP, ARP.
4. Network Access Layer
- What It Does: Deals with physical hardware, like cables and wireless signals, and frames data for transmission.
- Examples: Ethernet, Wi-Fi, PPP.
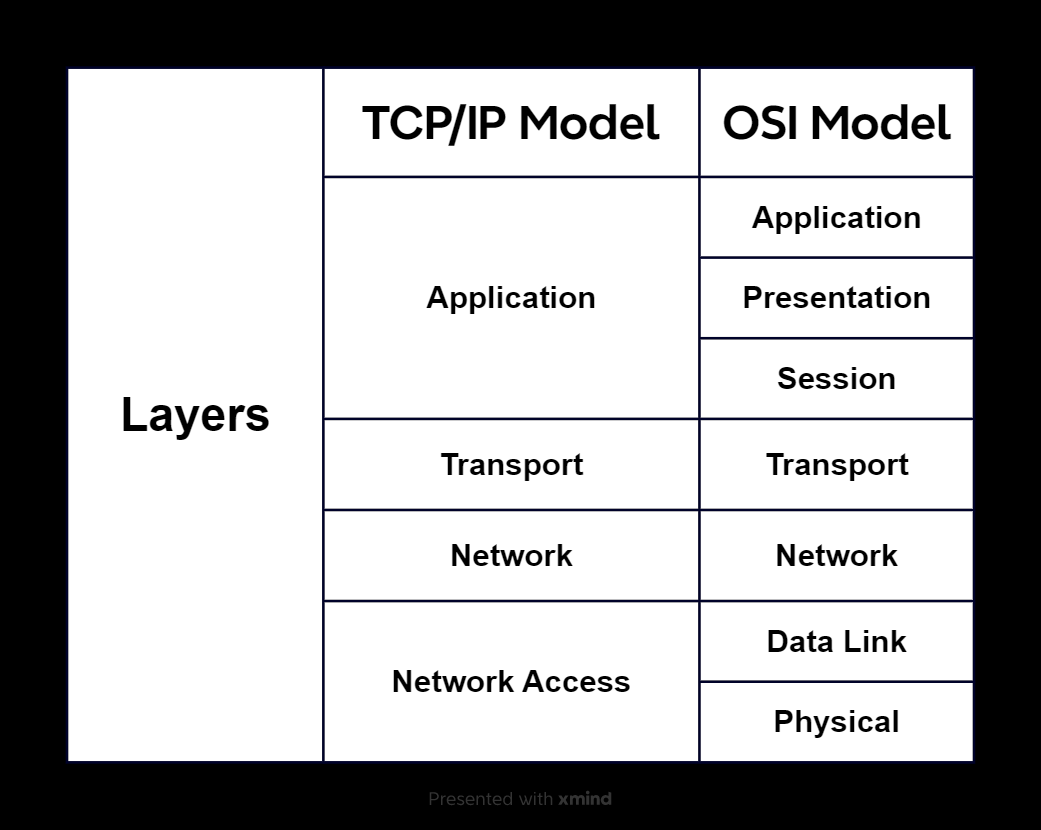
How Does TCP/IP Differ from OSI?
Here are the key differences between the TCP/IP and OSI models:
1. Number of Layers
- TCP/IP: Four layers
- OSI: Seven layers
2. Layer Functions
TCP/IP combines some of the OSI layers:
- The Application Layer in TCP/IP handles Layers 5 (Session), 6 (Presentation), and 7 (Application) from OSI.
- The Network Access Layer in TCP/IP combines Layers 1 (Physical) and 2 (Data Link) from OSI.
3. Design Philosophy
- OSI: Designed as a teaching tool to understand networking.
- TCP/IP: Focused on real-world implementation.
4. Adoption
The TCP/IP model is the backbone of the internet. The OSI model, while valuable for learning, isn’t used in practical implementations.
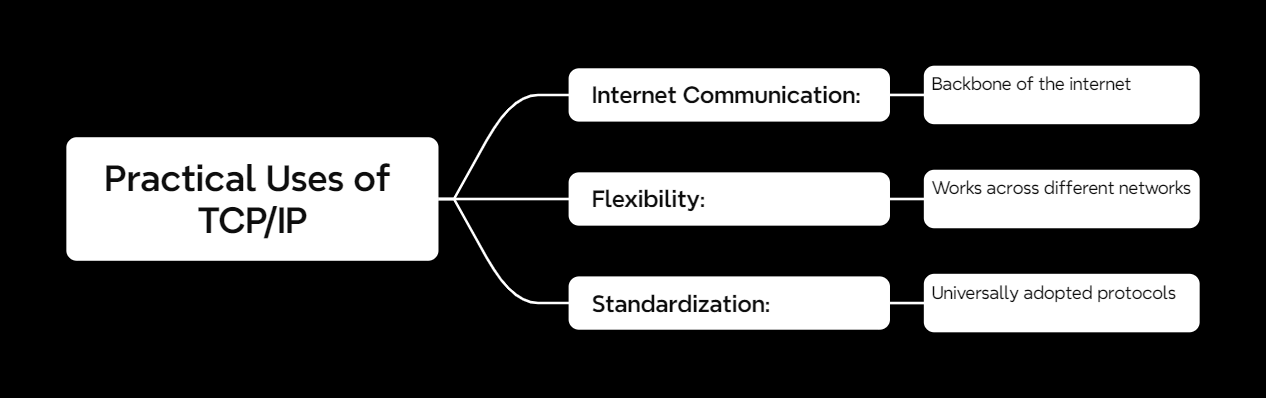
Why TCP/IP Is So Important
The TCP/IP model isn’t just theoretical—it’s the standard for how data moves across networks.
1. Internet Communication
Every time you send an email, stream Netflix, or browse memes, TCP/IP is working in the background.
2. Flexibility
It works seamlessly across different types of networks, whether wired or wireless.
3. Standardization
Thanks to TCP/IP, devices and systems worldwide can communicate without compatibility issues.